Migrating SAP BW to Kronos: A Hands-On Guide
Overview
In this blog post, we present a practical overview of migrating SAP BW scenarios using Kronos — codbex's modern data integration platform — onto modern platforms like Snowflake, SAP HANA, and even lightweight setups like H2 for local testing. For a broader, business-oriented view of this migration journey, check out our companion blog post: Migrating SAP BW with Kronos - From Legacy to Flexibility
🎥 Prefer watching instead of reading? Here's the complete video walkthrough.
Migration Summary
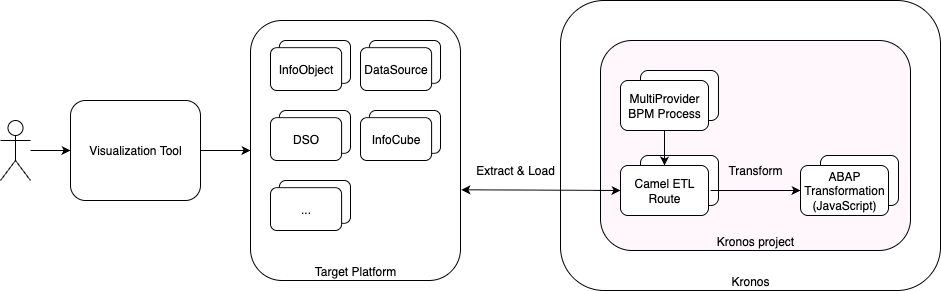
SAP BW systems, while historically robust, are built on tightly-coupled ABAP logic and rigid data models. Migrating to Kronos allows you to retain your BW logic while adopting modern, flexible, and cloud-native data platforms. Using Kronos, you can:
- Export and reimplement BW transformation logic.
- Replicate BW data models (InfoObjects, DataSources, DSOs, InfoCubes, MultiProviders).
- Rebuild data model flows logic with BPM orchestration.
- Visualize the result using modern tools.
- Run on Snowflake, HANA, PostgreSQL or even H2 for local testing.
The Kronos allows this entire process to be modular, reusable, and executable on any supported platform.
Lift-and-Shift Migration Approach
The "lift and shift" strategy provides a straightforward and transparent method to migrate your SAP BW logic with minimal redesign. The following steps outline the process using Kronos:
1. Replicate BW Objects to Target Platform
All BW objects (InfoObjects, DataSources, DSOs, InfoCubes, etc.) are copied over to the destination platform. This can be done using any data migration tools.
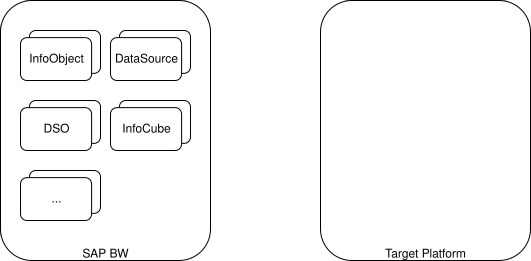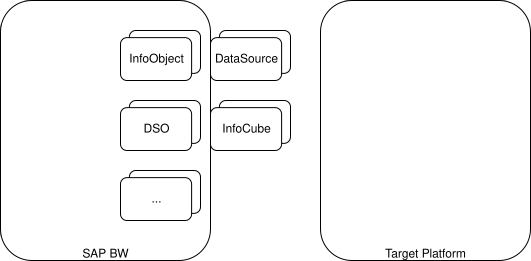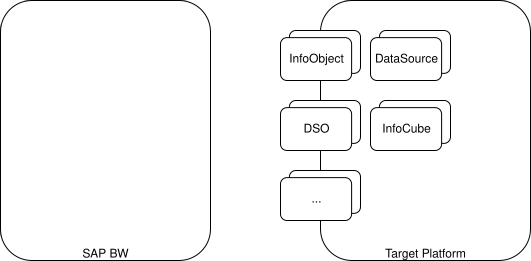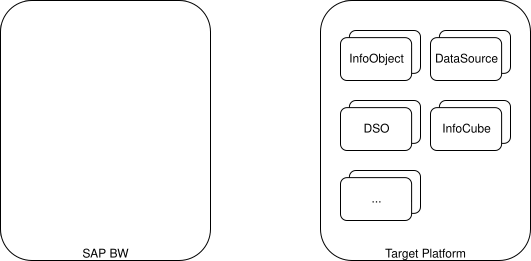
2. Migrate Data
Once the data structures are in place, all associated data must also be migrated to ensure full alignment with the original BW system. This step guarantees a one-to-one semantic correspondence between the source and target environments.
3. Export BW Transformation Logic
Each ABAP transformation is completely exported from the BW system using a dedicated export tool.
The exported artifacts must be pushed to a Kronos project stored in a git repository. 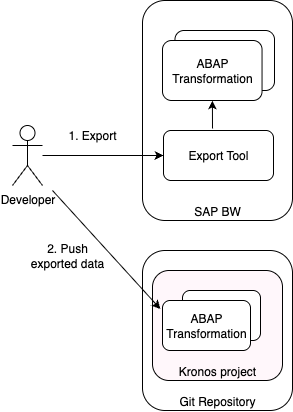
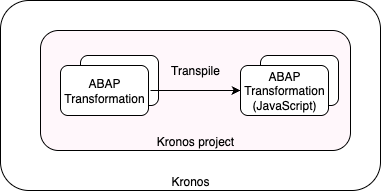
4. ABAP Transformation code to JavaScript code
On build time, the ABAP transformation code is automatically transpiled to JavaScript. This allows Kronos to execute it during the transformation.
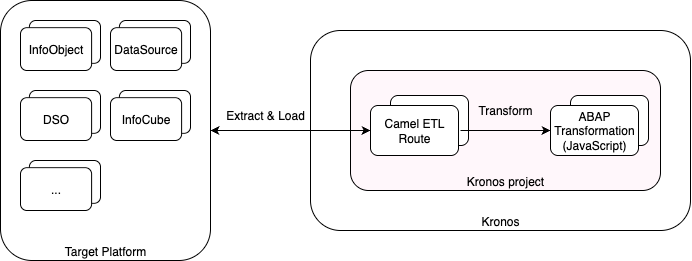
5. Rebuild Transformations as ETL Camel Routes
Using Kronos ETL modules based on Apache Camel, each transformation is re-implemented as a Camel route.
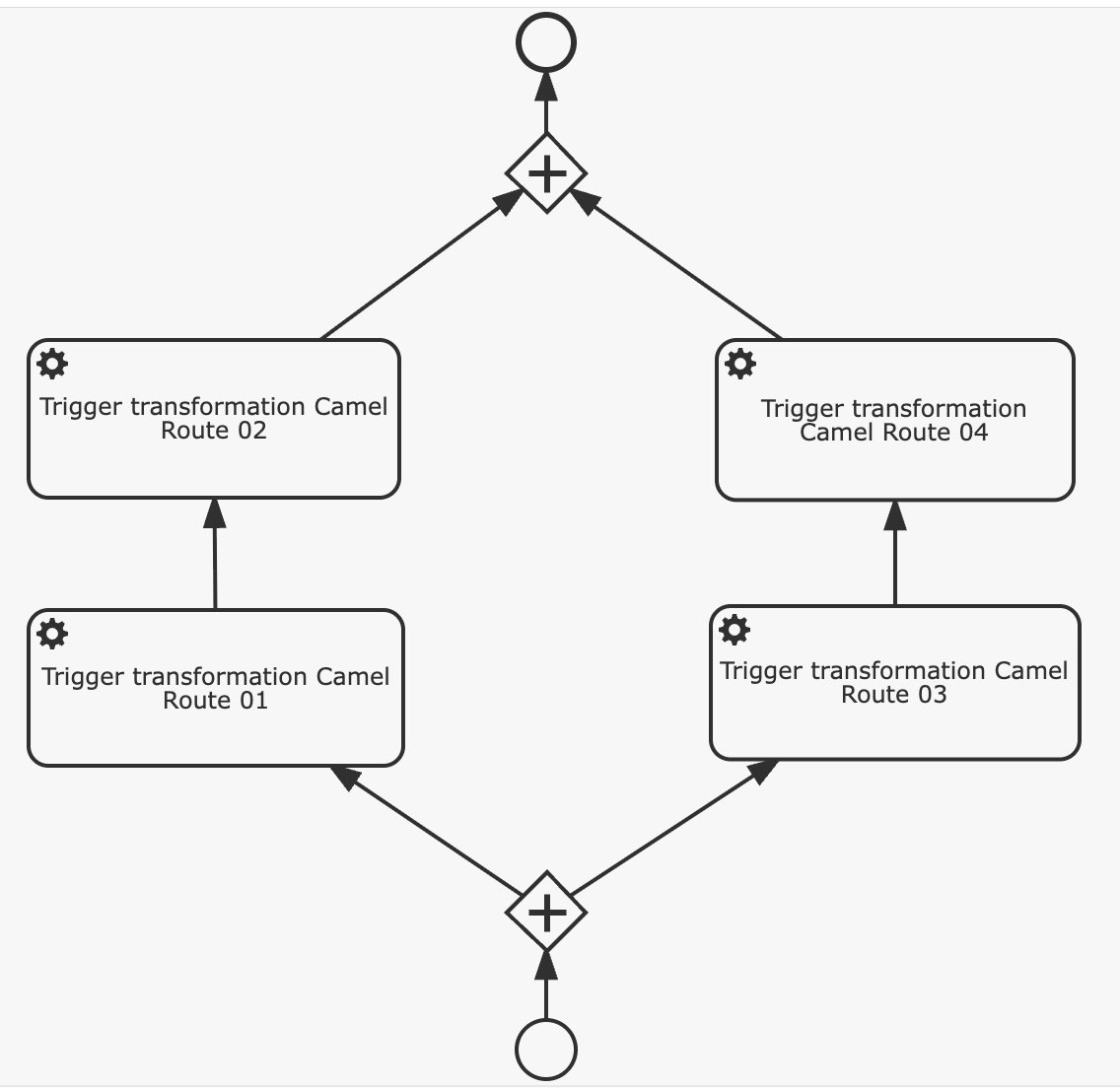
6. BW Data Model Flows as BPM Processes
Each data model flow is implemented as Kronos BPM process:
- Each BPM task calls an ETL Camel route
- Aggregated results are stored
- Fully orchestrated execution flow mirrors BW's data model flow behavior
7. Visualization
Once all BPM processes have been executed and the underlying ETL transformations have run successfully, the data is ready for visualization. At this stage, you can:
- Connect to modern BI tools like Tableau, Power BI, or Apache Superset
- Recreate classic BEx Queries using Kronos or redesign reports with a modern UX
- Enable self-service analytics and dynamic dashboards powered by the transformed, consolidated data
8. Decommission the BW System
Once all data structures, transformations, and reporting flows have been successfully migrated and validated within Kronos, the legacy SAP BW system can be safely decommissioned. This marks the completion of the migration, allowing you to reduce infrastructure costs and eliminate technical debt associated with maintaining the older BW environment.
Demo: Bike Sales Data Flow Migration
To demonstrate the Kronos-based SAP BW migration approach, we've prepared a complete demo scenario showcasing the migration of a BW data flow related to Bike Sales. This scenario illustrates how a typical end-to-end pipeline — from raw DataSources to final processed data — can be rebuilt using Kronos components.
Scenario Overview
This scenario outlines the data flow architecture for reporting bike sales through two distinct sales channels: Internet Sales and Reseller Sales. The architecture is designed in SAP BW using standard InfoProviders and transformation logic to support unified and channel-specific reporting.
Sales Channels:
- Internet Sales
- Reseller Sales
Each channel has its own independent data acquisition and processing pipeline, yet they are ultimately consolidated for unified analysis.
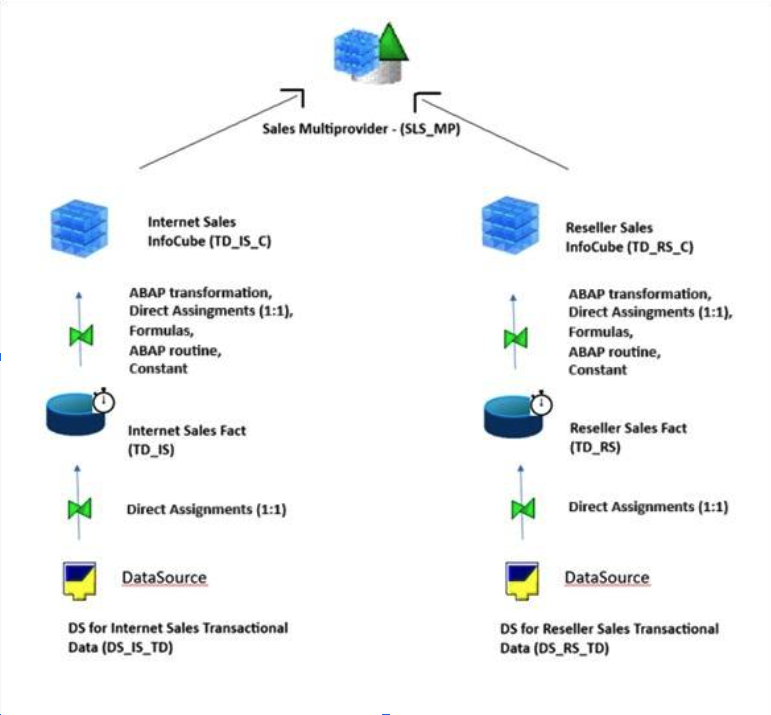
Data Flow Description:
- Data Sources:
- DS for Internet Sales Transactional Data (DS_IS_TD): Captures transactional data related to online (internet-based) sales.
- DS for Reseller Sales Transactional Data (DS_RS_TD): Gathers transactional sales data from reseller partners.
These data sources serve as the initial entry point of raw sales data into the SAP BW system.
- Data Targets (ODS Layer / DataStore Objects):
- Internet Sales Fact (TD_IS)
- Reseller Sales Fact (TD_RS)
Transactional data is loaded 1:1 into these DataStore Objects. These represent the consolidation layer where data is cleansed and harmonized before being pushed into analytical InfoCubes.
- InfoCubes (Analytical Layer):
- Internet Sales InfoCube (TD_IS_C)
- Reseller Sales InfoCube (TD_RS_C)
Data is transferred from the facts layer into the InfoCubes using direct assignments (1:1), formulas and abap routines, allowing for the enrichment of key figures and characteristics needed for reporting. These cubes store aggregated sales data for each channel, optimized for performance and analysis.
- Consolidation for Reporting - Sales Multiprovider (SLS_MP)
The InfoCubes for both Internet and Reseller Sales are combined into a Multiprovider, enabling a unified view of total sales. This allows users to:
- Analyze sales by channel, region, time, product, and customer.
- Compare performance between Internet and Reseller sales.
- Generate comprehensive reports for management insights.
You can find more details about the scenario in the description file here.
Sample Project Implementation
This section outlines how the Bike Sales data flow scenario is implemented in the sample Git repository. While the scenario can run on any supported target platform — including Snowflake, PostgreSQL, and SAP HANA—it is described using the H2 Database for simplicity and ease of local execution.
Each step demonstrates how core components—such as table structures, transformation logic, and orchestration flows—are realized using Kronos, following the principles of the lift-and-shift migration approach.
Start Kronos instance locally
Start a Kronos container locally using the following command:
docker run --name codbex-kronos \
-p 80:80 -p 8081:8081 \
ghcr.io/codbex/codbex-kronos:2.99.0By default, Kronos uses the H2 database as the target platform, making it easy to run the demo locally without additional setup. No configuration changes are required to get started.
Run the Sample Project
Once the Kronos instance is up and running, you can open and run the sample project using the following steps:
Open Kronos in your browser at http://localhost/
Login using the default credentials, user
adminand passwordadmin
Go to the
Gitperspective
Click on the
Clonebutton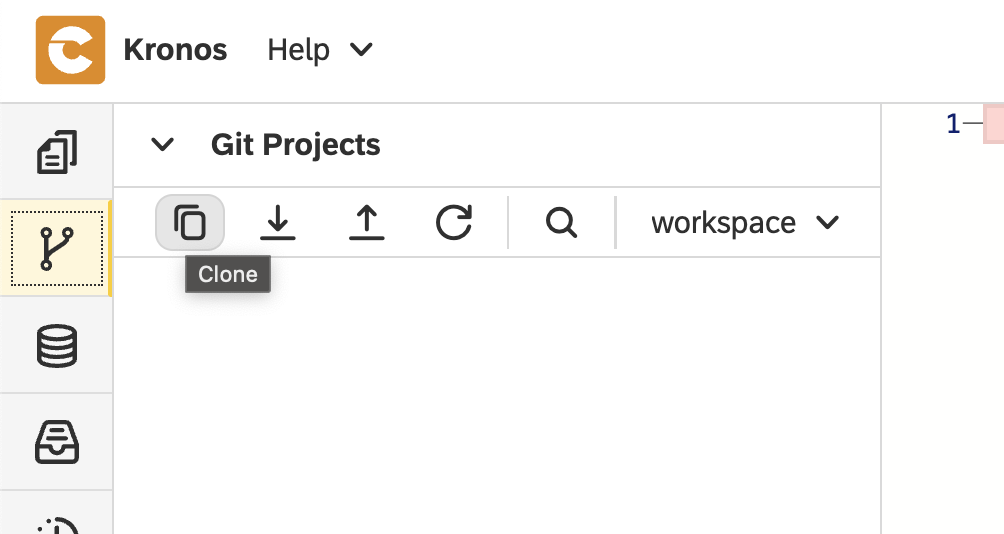
Set
https://github.com/codbex/codbex-sample-kronos-bw-sales-migration.gitfor repository URL and click on theClonebutton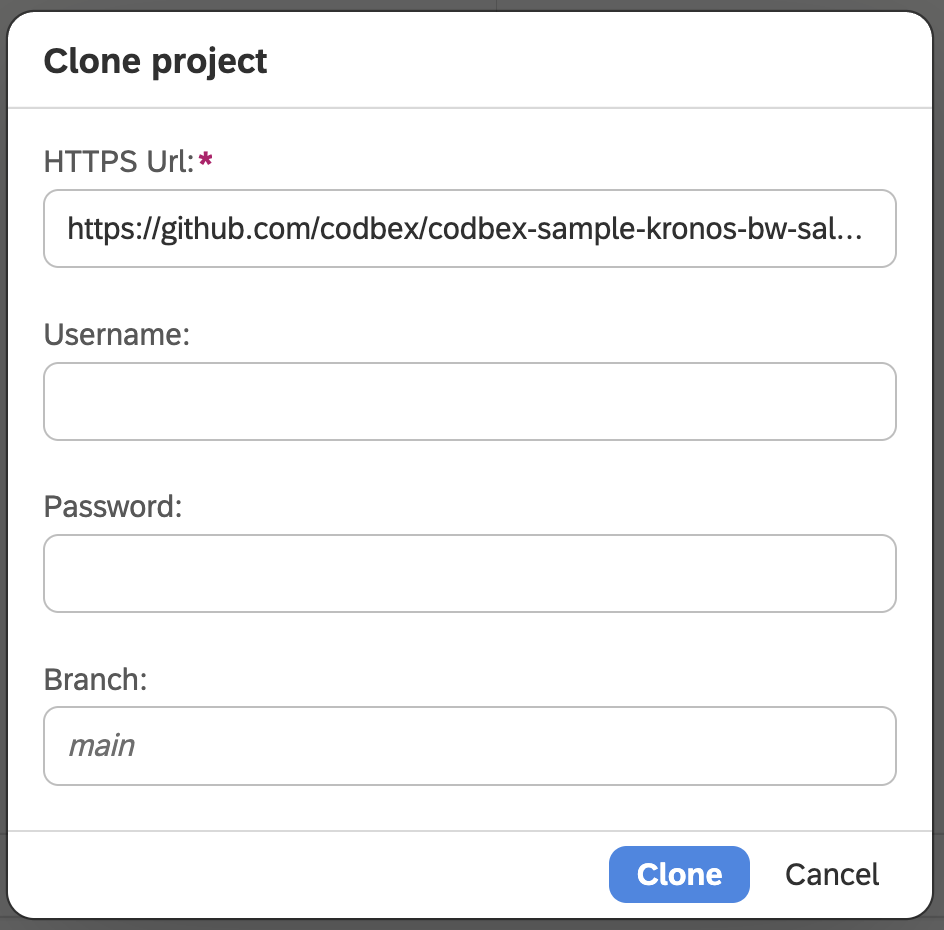
Go back to the
Workbenchperspective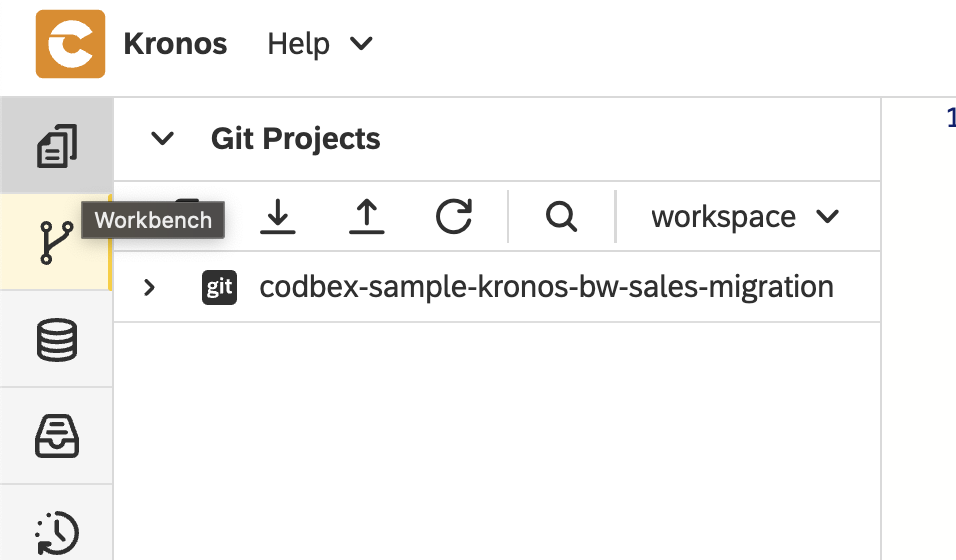
Click on the
Publish allbutton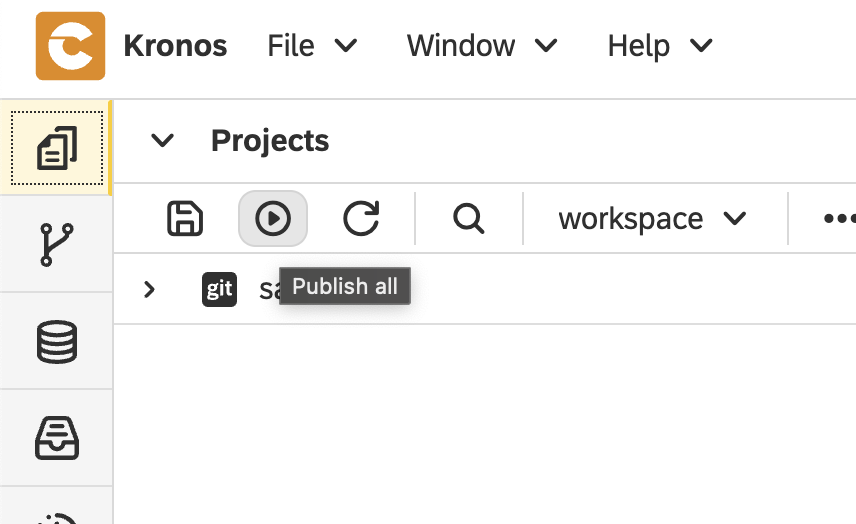
Publishing the project activates it in the Kronos runtime. This step automatically sets up all required components, including database structures, sample data, transformation logic, BPM processes, etc.—so everything is ready to run without additional configuration.
Since this is an asynchronous process, it may take a few seconds for all components to be fully initialized.
Define BW Objects in the Target Platform
To simplify the setup and avoid using external data migration tools, all BW structures used in the scenario—such as tables for DataSources, DSOs, and Cubes—are predefined in the Kronos Database Schema Model (DSM) file: sales/db/db-schema.dsm: 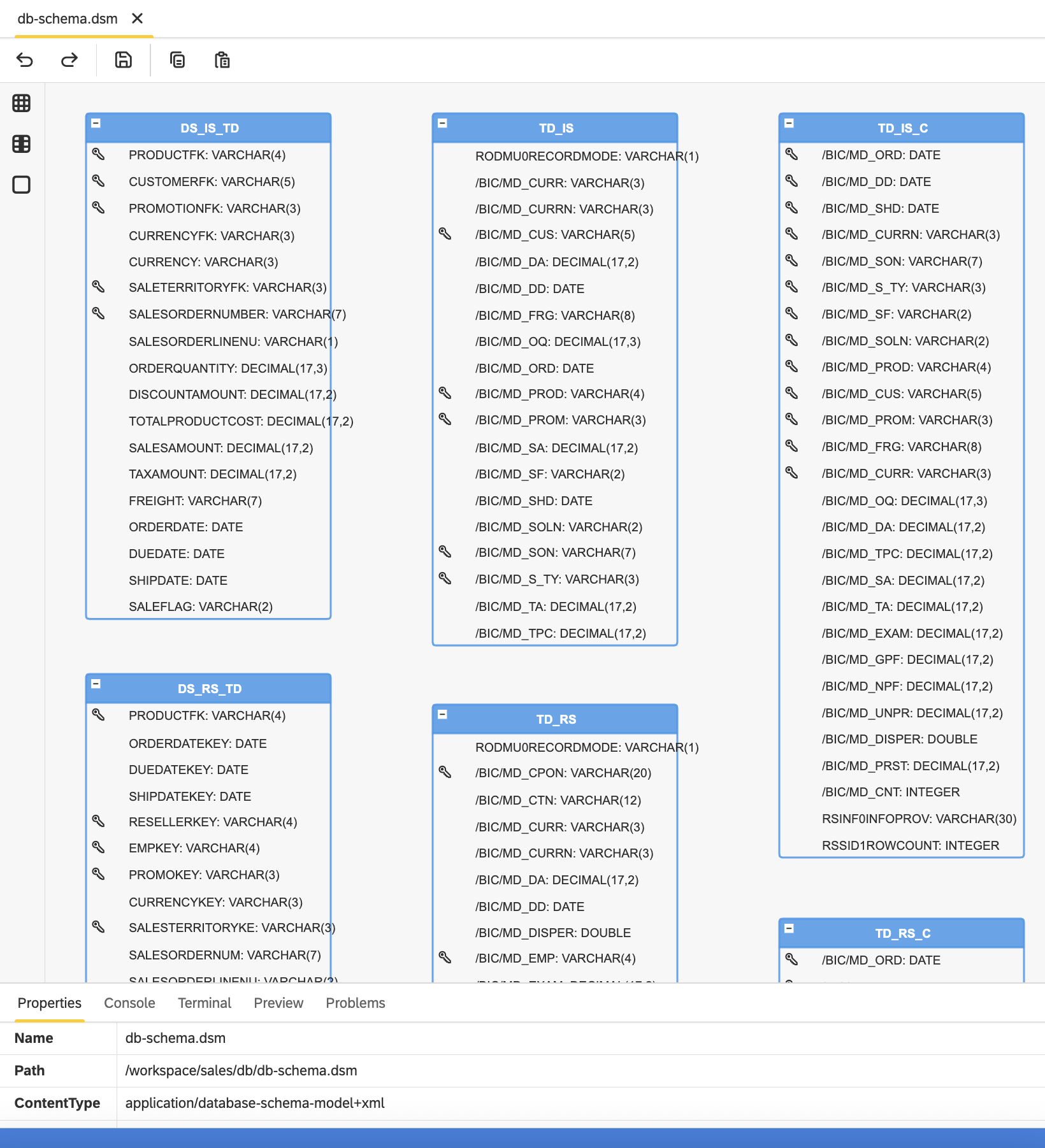
This schema is automatically applied when the project is published, creating all required tables in the target platform with no manual setup needed.
Import Sample Data
Following the same approach, sample data for the scenario is provided as CSV files located in dir: sales/db/
These CSV files are automatically imported into the target platform during project publishing. This makes it possible to initialize the environment without relying on any external data migration tools.
All CSV files which are used are configured in CSVIM file sales/db/data.csvim
✅ This simplified setup works out of the box across supported platforms, including H2, Snowflake, PostgreSQL, and HANA.
Export BW Transformation Logic
The ABAP transformation logic originally defined in SAP BW is exported using a dedicated export tool. In the sample project, the exported transformations are stored as .abap files in the following directory: sales/src/
Transpile ABAP to JavaScript
When the project is published in Kronos, the exported ABAP transformation logic from dir sales/src/ is automatically transpiled to JavaScript. This makes it executable within Kronos during ETL processing.
The transpilation is triggered by the build scripts defined in the project's configuration file sales/project.json when the project is published.
The generated JavaScript files are stored in the sales/dist/ folder of the project. 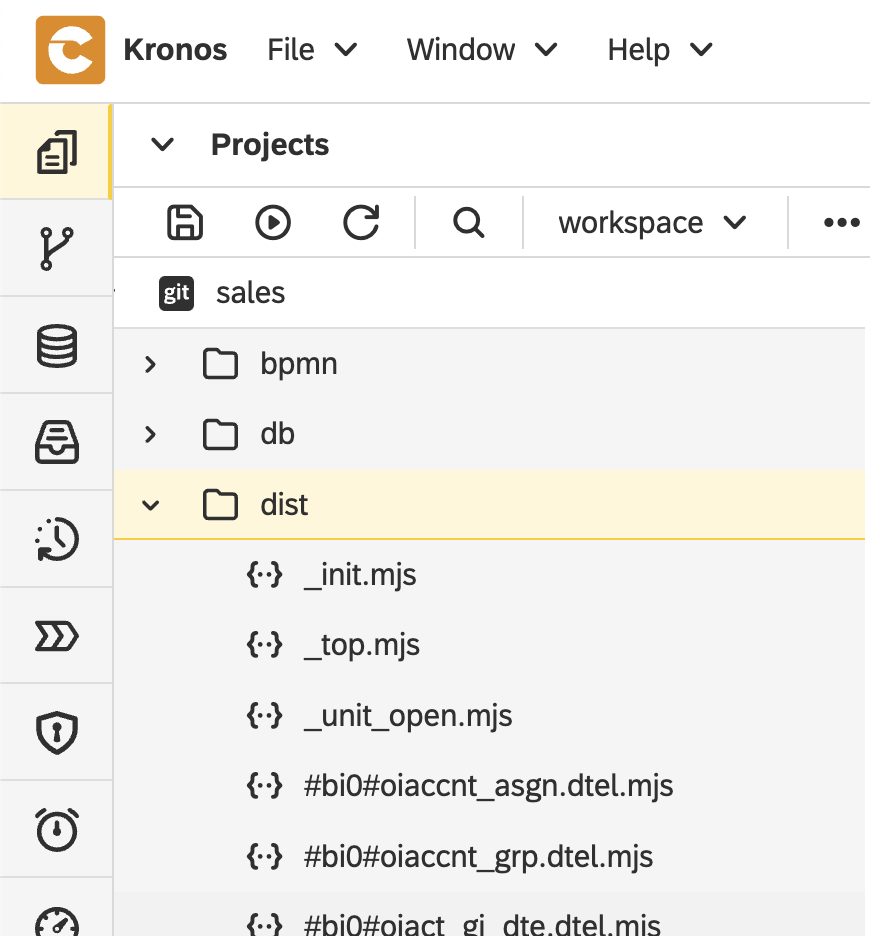
Rebuild Transformations as ETL Camel Routes
Each transformation in the sample scenario is implemented as a reusable ETL Camel route located at sales/etl/etl-route.camel. The route perform a simplified Extract → Transform → Load flow:
- The extract step reads all data from the source table (full load used for simplicity) - sales/etl/data-extractor.ts
- The transform step invokes the corresponding transpiled ABAP transformation logic (in JavaScript) sales/etl/transform-entries.ts
- The load step writes the transformed results into the defined target table sales/etl/data-loader.ts
Each step uses helper functions implemented in sales/etl/etl.ts. These functions leverage the codbex Database API to access and manipulate data.
The route itself is parameterized — it accepts the source table, target table, and transformation ID as exchange properties, allowing it to be reused across different flows.
Here’s what the assembled route looks like: 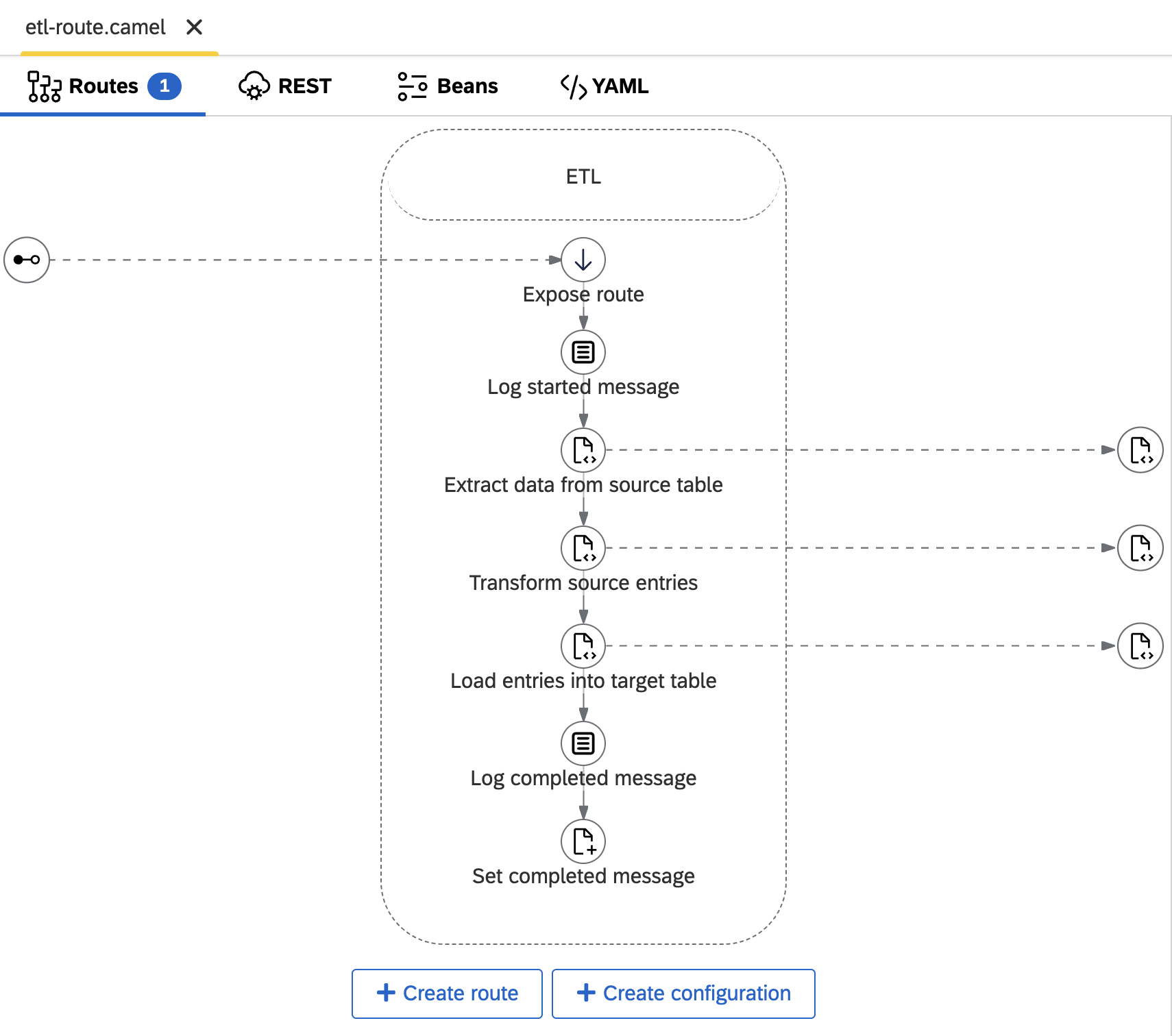
💡 Want to implement your own route? Check out our Tips & Tricks for the Integration Modeler.
Model BW Data Flows as BPM Processes
In SAP BW, data flows are often tightly orchestrated—from DataSources through DSOs to Cubes or MultiProviders—in a specific execution sequence. To replicate this orchestration in Kronos, these flows are reimplemented as BPM processes that preserve the original order of execution.
In the demo project, this flow is modeled in the BPM file sales/bpmn/sls_mp.bpmn. 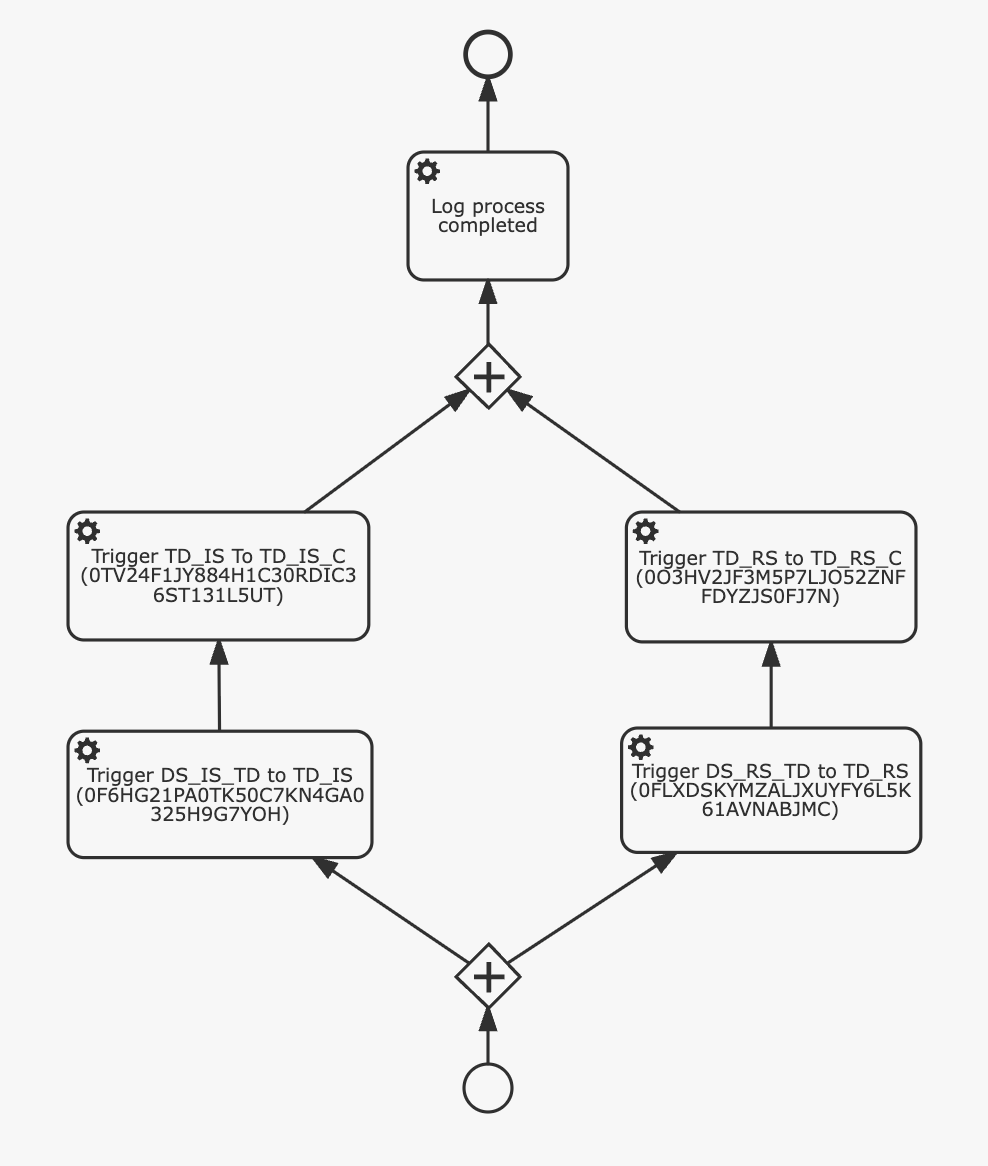
Each BPM task:
- Triggers the defined in the previous step ETL Camel route
- Passes different parameters for source/target table names and the transformation ID depending on the current step
The BPM tasks themselves are stored in the sales/bpmn folder. Each task uses the codbex Integrations API to programmatically trigger the route execution.
This approach ensures a 1:1 match with the original BW process chains, while offering clean modularity in Kronos. 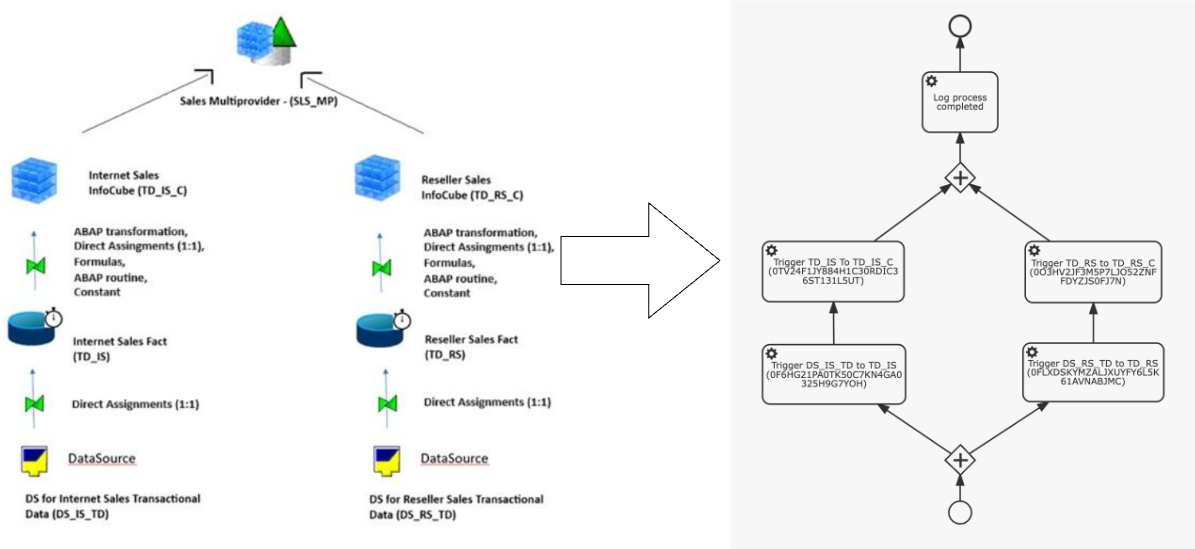
Using BPM in Kronos comes with additional benefits:
- Visual monitoring of running process instances
- Status tracking, including step-level success/failure
- Easy error inspection
- Ability to retrigger failed processes
All of this is available in the Processes perspective, providing clear operational insight and control over data flows.
💡 Want to build your own BPM flow? Check out our BPM Modeler Tips & Tricks to get started.
Run the Data Flow via BPM Process
Once everything is published, the full data pipeline—modeled as a BPM process—can be executed through a dedicated UI form:
- A simple user-facing form is modeled in the file: sales/sls_mp-process.form
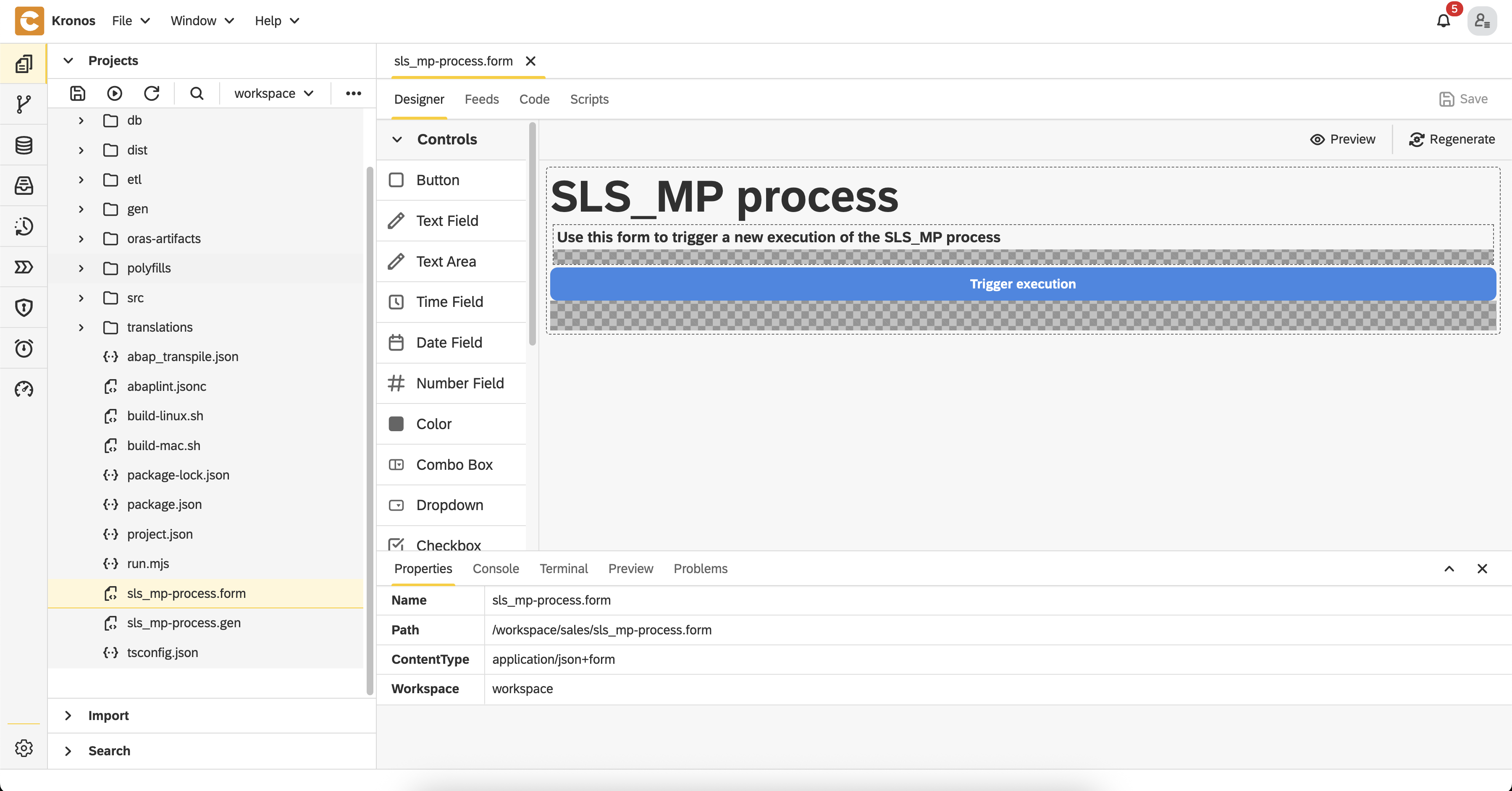
- When you open the form and click the
Regeneratebutton, the corresponding UI is generated in the sales/gen directory - To access the form, open this URL in your browser: http://localhost/services/web/sales/gen/sls_mp-process/forms/sls_mp-process/index.html
- Click the
Trigger executionbutton in the form UI to start the process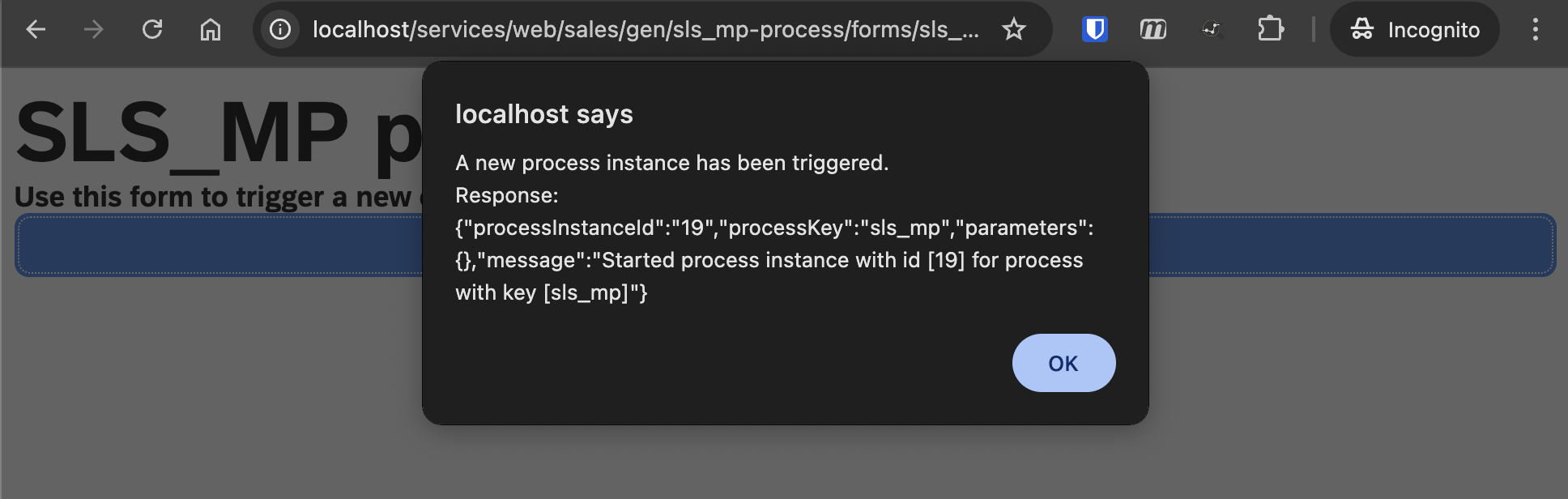
- You can monitor the progress and status of the execution in the Processes perspective within Kronos
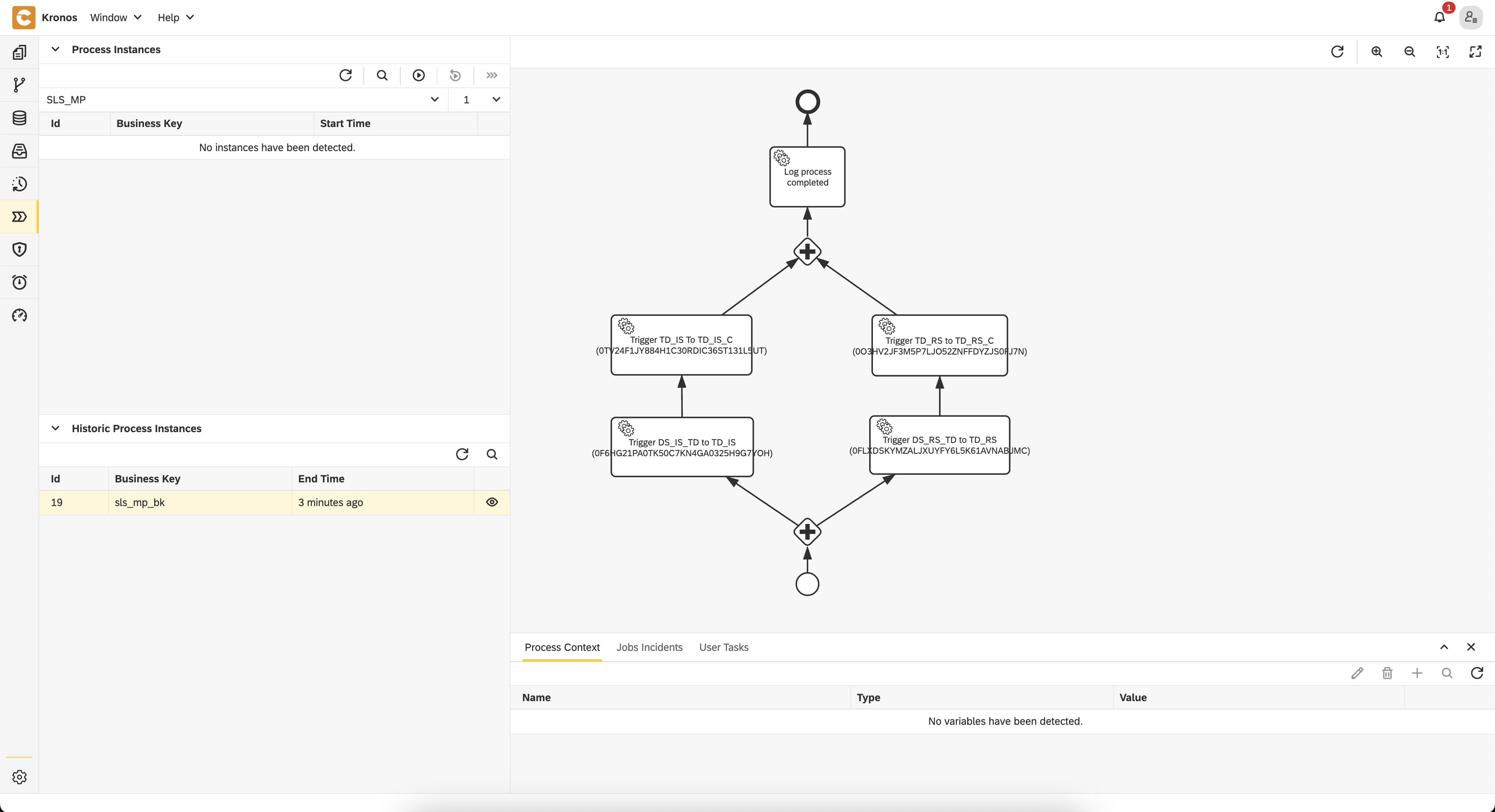
✅ Once the process completes successfully:
- The cube tables
TD_RS_CandTD_IS_Cwill contain the final output data - You can explore the results using SQL in the Database perspective:sql
SELECT * FROM TD_IS_C LIMIT 50; SELECT * FROM TD_RS_C LIMIT 50;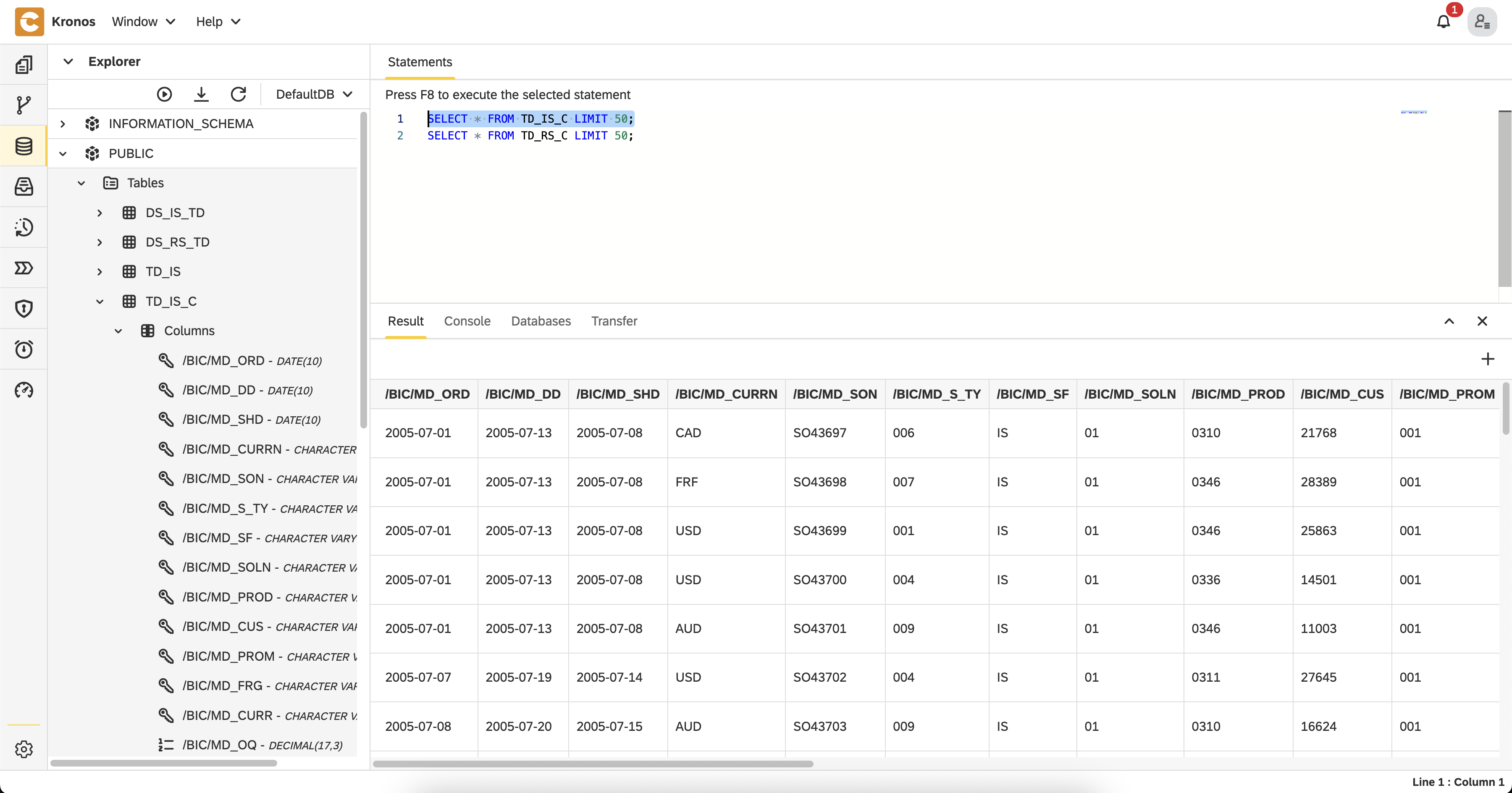
This form-based interface offers a simple way to trigger the full BW data flow. Alternatively, the same process can be triggered programmatically using the codbex SDK, enabling automation scenarios such as scheduled execution via cron jobs, integration from other BPM processes, external API calls, etc. This provides flexibility for both manual and automated orchestration, while still preserving full visibility and control over the execution lifecycle.
Data Visualization (Coming Soon)
Once all data structures are defined, transformations executed, and data flows orchestrated—your data is fully prepared for visualization.
While visualization is not covered in this post, it's an essential final step of any BI landscape. Whether you aim to replicate classic BEx Queries, build interactive dashboards, or plug into modern BI tools like Power BI, Tableau, or Apache Superset — the processed data is ready for it.
📌 Visualization is the essential next step. We’ve covered it in detail in our follow-up blog: Visualizing Kronos Data on Snowflake with Power BI, where we show how to connect Power BI directly to Snowflake and build real-time dashboards.
Wrapping Up — From BW to Kronos, Made Simple
This guide walked through how Kronos can power a structured, modular, and executable migration of SAP BW data models — covering everything from ABAP transformation logic to ETL pipelines and BPM process orchestration.
By following a lift-and-shift approach, clients can migrate their existing BW logic and data structures onto modern platforms like Snowflake, SAP HANA, PostgreSQL, or even H2 for local testing — often in a remarkably short time frame. The approach emphasizes preserving business logic while gaining the flexibility and scalability of cloud-native tools.
With Kronos, organizations can:
- Start small and scale gradually
- Run projects locally or deploy directly to the cloud
- Preserve original BW logic with minimal rework
- Automate, monitor, and control the entire data pipeline visually
🚀 Want to try it yourself?
Getting started with Kronos is easy—whether locally or in the cloud. For example, it’s available in the Snowflake Marketplace with a free trial, making installation and onboarding a matter of minutes.
💬 Questions or business inquiries?
We'd love to hear from you. Reach out via our contact page.